Cross-Chain Swaps: Revolutionizing Blockchain Interoperability
TL;DR
Introduction to Cross-Chain Swaps: Cross-chain swaps are a critical innovation in blockchain technology, offering interoperability between different blockchain networks. They enable seamless asset exchanges across various blockchains, enhancing the functionality and reach of decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and decentralized applications (dApps).
How Cross-Chain Swaps Work: These swaps rely on technologies like smart contracts and Hash Time-Locked Contracts (HTLCs), with mechanisms like atomic swaps and bridge protocols facilitating the process. Innovations like decentralized oracle networks, liquidity pools, and advanced protocols like LayerZero are further advancing these technologies, making them more efficient and secure.
Impact and Top Projects in Cross-Chain Swaps: Cross-chain swaps significantly increase blockchain interoperability, with projects like LayerZero, Axelar, Chainlink, and InterPort Finance leading in this space. Horizen EON exemplifies the integration of these technologies, focusing on user experience and enhanced interoperability, illustrating the potential and future direction of blockchain technology.
Introduction to Cross-Chain Swaps
Cross-chain swaps stand as a pivotal innovation in the blockchain pace, offering interoperability between different blockchain networks. These swaps enable seamless asset exchanges across diverse blockchains, propelling the decentralized finance (DeFi) sector towards a more interconnected future.
What are Cross-Chain Swaps?
Cross-chain swaps represent a cutting-edge concept in the blockchain universe, designed to facilitate direct transfers of digital assets across different blockchain networks. These swaps are the key to solving one of the most significant challenges in the blockchain sector: interoperability.
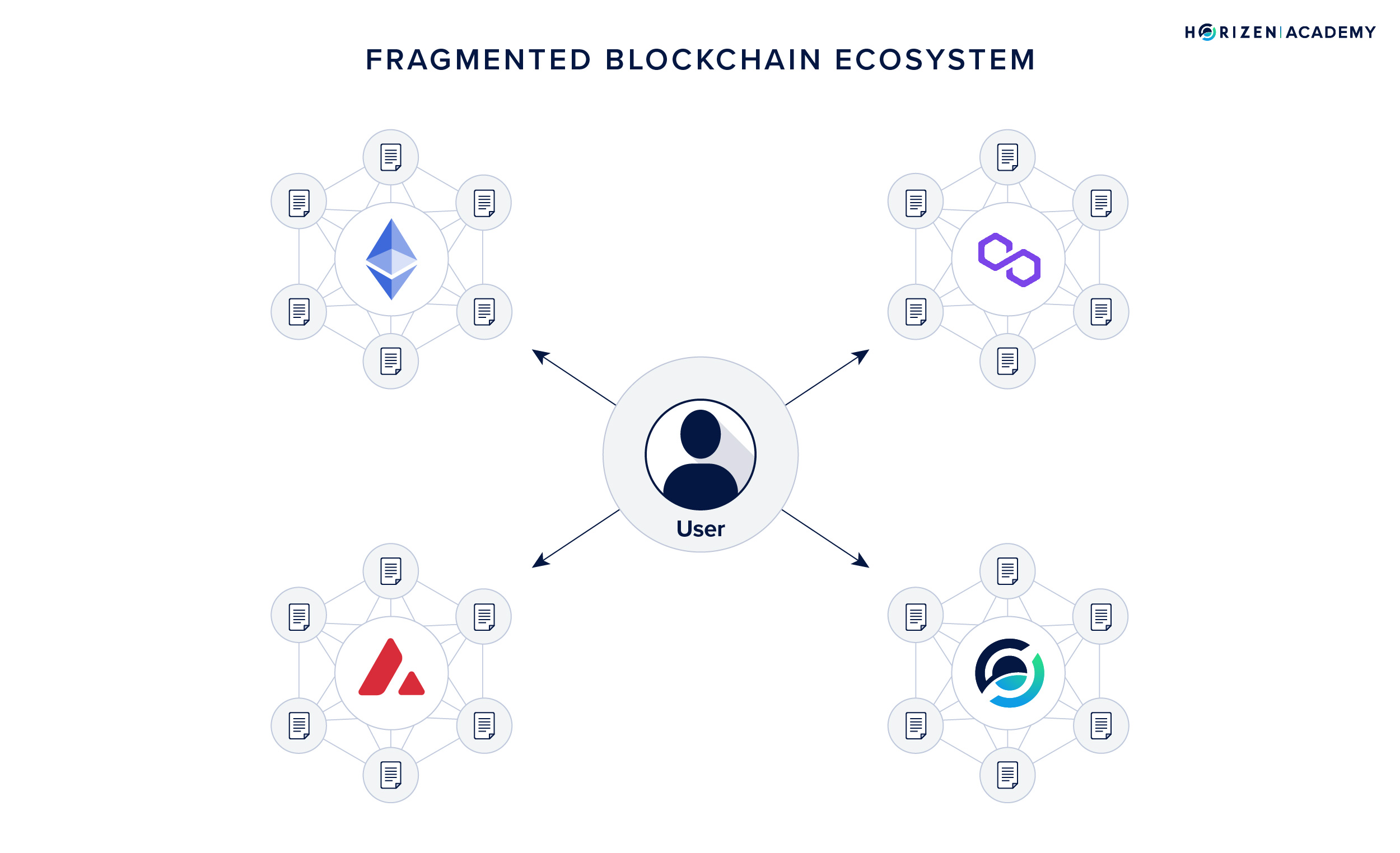
The Need for Cross-Chain Swaps
Traditionally, blockchain networks operate in isolation, each functioning within its ecosystem. This siloed nature hinders the free flow of assets, information, and value between different blockchains. Cross-chain swaps emerge as a solution, enabling a fluid exchange of assets across these isolated networks, thus enhancing the utility and accessibility of blockchain technology.
Impact on the Blockchain Ecosystem
By enabling asset transfers across various blockchains, cross-chain swaps significantly broaden the scope of blockchain technology. They make it feasible for users to engage with multiple blockchain networks without being restricted to the capabilities or assets of a single chain. This advancement has profound implications for decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and the broader scope of decentralized applications (dApps).
How Do Cross-Chain Swaps Work?
The operational framework of cross-chain swaps is complex, involving several technological components and mechanisms to ensure secure and efficient transactions across disparate blockchain networks.
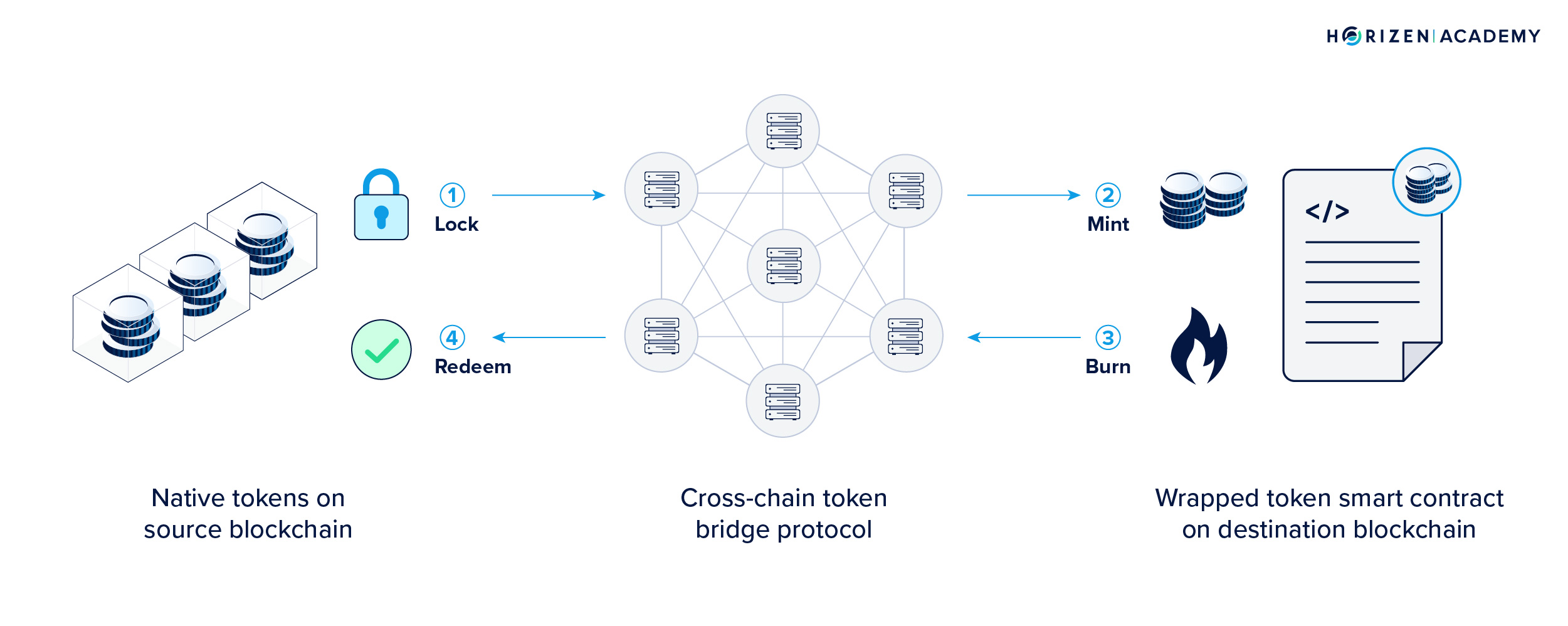
Understanding the Technical Foundations
- Smart Contracts: At the heart of cross-chain swaps lie smart contracts – self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code. These contracts operate autonomously, without the need for intermediaries, ensuring trust and security in transactions.
- Hash Time-Locked Contracts (HTLCs): A key component of many cross-chain swaps, HTLCs add a time-bound element to transactions. They require the recipient of a transaction to acknowledge receiving the payment within a certain timeframe by generating a cryptographic proof of payment. If the recipient fails to confirm the transaction within the stipulated period, the funds are returned to the sender. This mechanism is fundamental in atomic swaps.
The Mechanics of Cross-Chain Swaps
- Atomic Swaps: These involve two parties agreeing to trade tokens from different blockchains. Using HTLCs, atomic swaps ensure that either both parties successfully exchange tokens, or neither does, hence the term 'atomic'. This method eliminates counterparty risk but requires both blockchains to support the same cryptographic hash function.
- Bridge Protocols: Acting as intermediaries, bridge protocols create a link between two different blockchains. They often employ a "lock-and-mint" or "burn-and-mint" mechanism. In this process, tokens are either locked in a smart contract on the original chain and equivalent tokens are minted on the target chain, or they are burned on the source chain and recreated on the destination chain. These bridges facilitate the transfer of assets from one blockchain to another, expanding the utility and reach of digital assets.
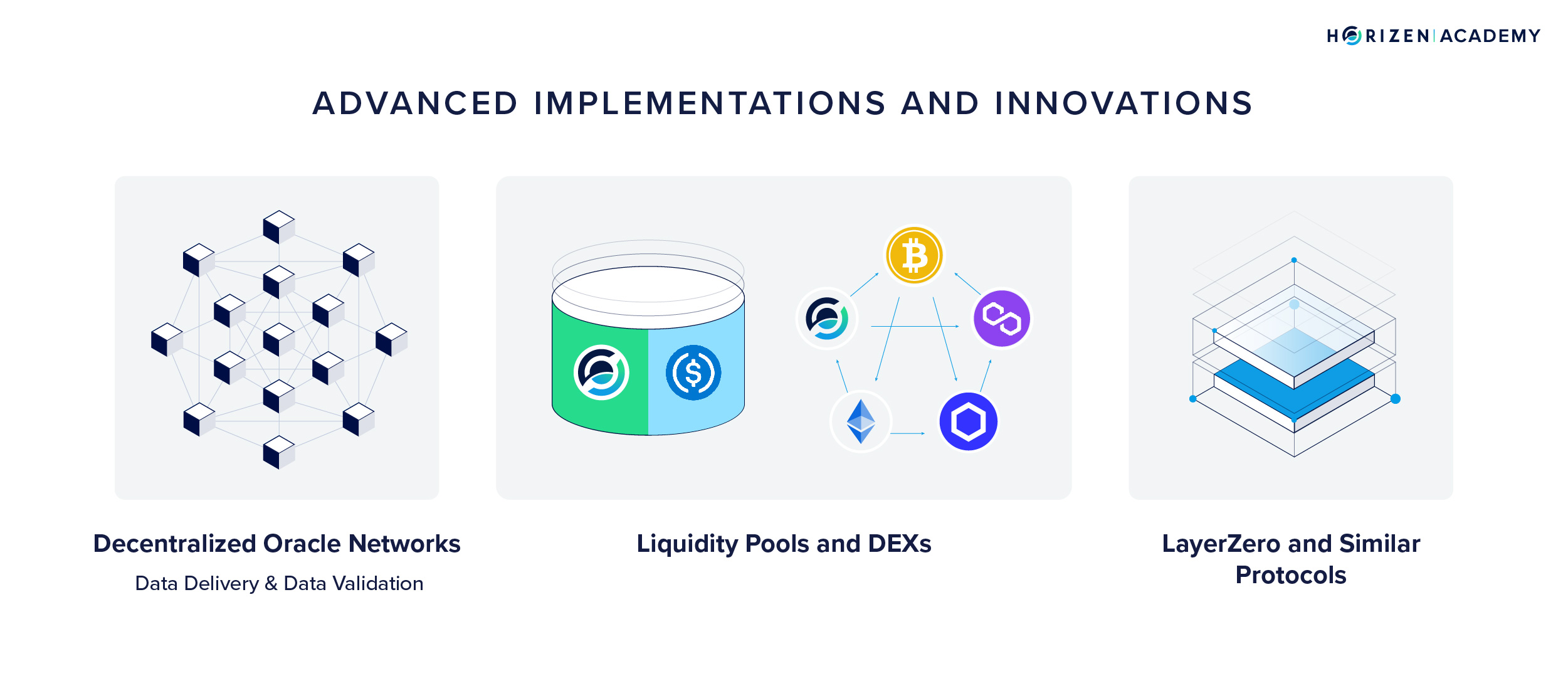
Advanced Implementations and Innovations
- Decentralized Oracle Networks: Projects like Chainlink are advancing cross-chain swap technology by using decentralized oracle networks. These networks provide reliable, tamper-proof inputs and outputs for complex smart contracts on any blockchain, enhancing the efficiency and security of cross-chain swaps.
- Liquidity Pools and DEXs: Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and liquidity pools are integral to cross-chain swaps. They provide the necessary liquidity for asset exchanges, facilitating seamless swaps without the need for traditional market makers.
- LayerZero and Similar Protocols: Technologies like LayerZero go beyond basic asset transfers, enabling arbitrary message passing across chains. This capability allows for more complex interactions, such as executing smart contract calls across different blockchains, thus broadening the scope of cross-chain swaps.
Pros & Cons of Cross-Chain Swap Systems
Cross-chain swaps, essential for enhancing interoperability in the blockchain space, employ various systems, each with unique mechanisms and attributes. Here's a detailed exploration of the most prominent systems:
1. Atomic Swaps
Mechanism: Atomic swaps involve two parties agreeing to trade tokens across different blockchains. They use Hash Time-Locked Contracts (HTLCs) which require both parties to acknowledge the receipt of funds within a specified timeframe, ensuring simultaneous execution or cancellation of the transaction.
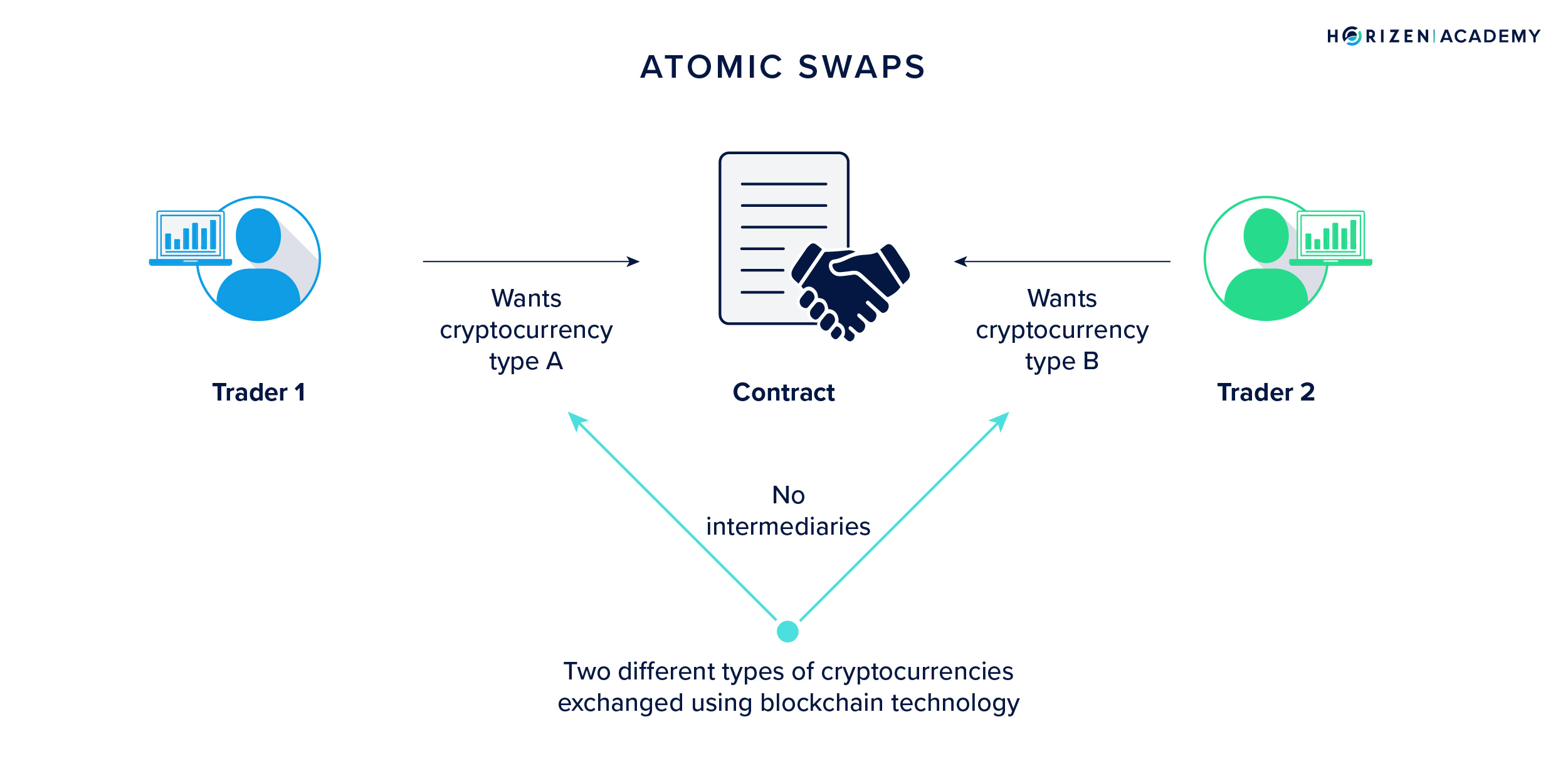
Pros:
- Decentralization: No need for intermediaries, aligning with the ethos of blockchain.
- Security: HTLCs ensure that transactions are either completed fully or reverted, mitigating risks of one-sided asset loss.
- Privacy: Transactions are direct between parties, enhancing privacy compared to centralized exchanges.
Cons:
- Complexity: Technical expertise is required to initiate and execute atomic swaps.
- Limited Scalability: Challenges in matching parties and assets across various chains.
- Compatibility Issues: Requires compatible scripting languages and hash algorithms on participating blockchains.
2. Bridge Protocols
Mechanism: Bridge protocols create a connection between two blockchains, allowing tokens from one blockchain to be 'locked' and a corresponding representation to be 'minted' on another blockchain, thus facilitating the swap.
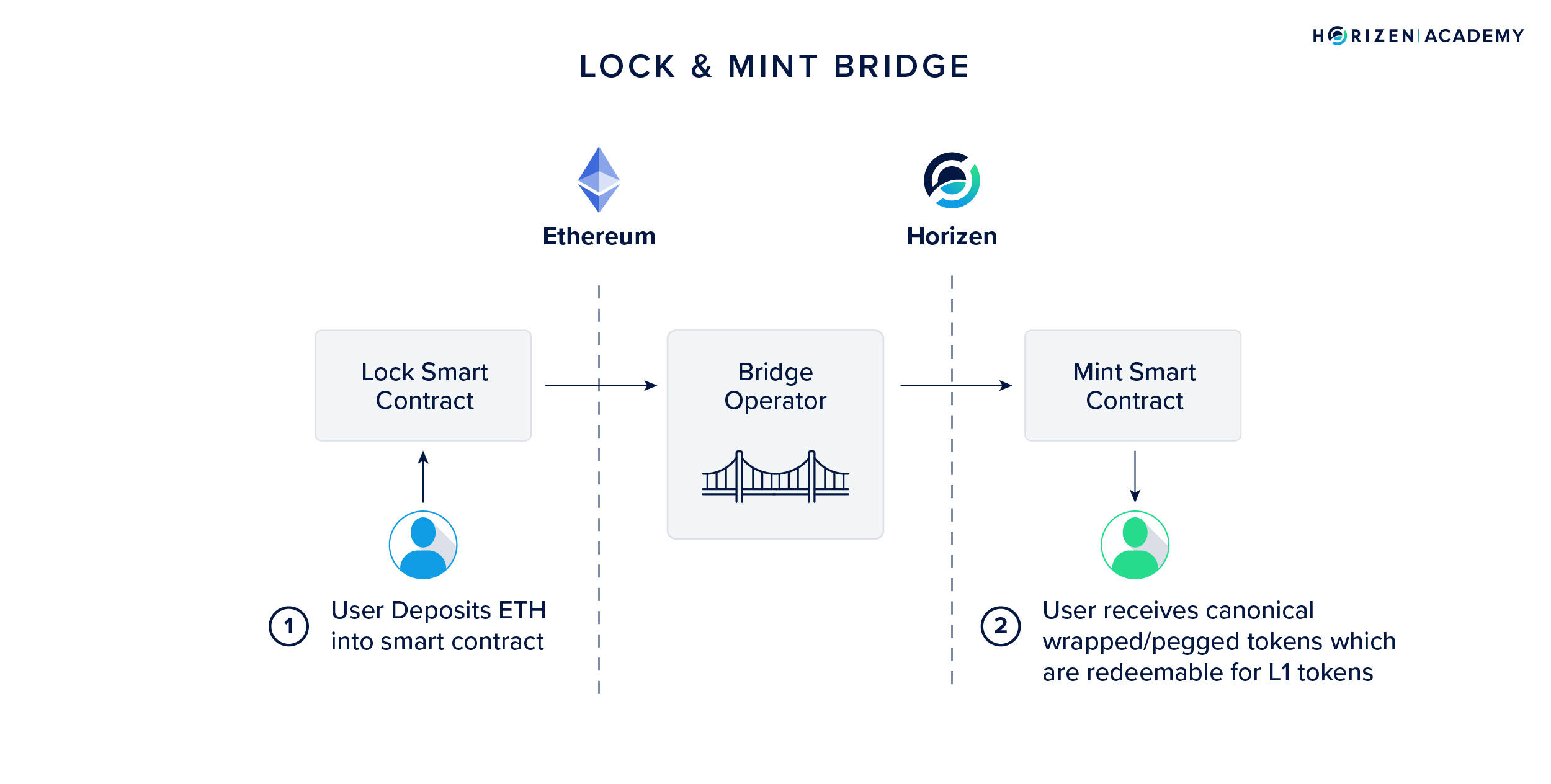
Pros:
- Broad Accessibility: Bridges support a wide range of tokens and blockchains.
- Liquidity: They enhance liquidity by connecting isolated blockchain ecosystems.
- User Experience: Often more straightforward for the average user than atomic swaps.
Cons:
- Centralization Risk: Some bridges may have centralized control points, contradicting blockchain decentralization principles.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Bridges have been targets of attacks, risking user funds.
- Reliance on External Infrastructure: Dependence on the bridge's integrity and longevity for asset security.
3. LayerZero's Omnichain Interoperability Protocol
Mechanism: LayerZero provides a platform for cross-chain communication, using an omnichain approach to enable users to interact with multiple blockchains seamlessly.
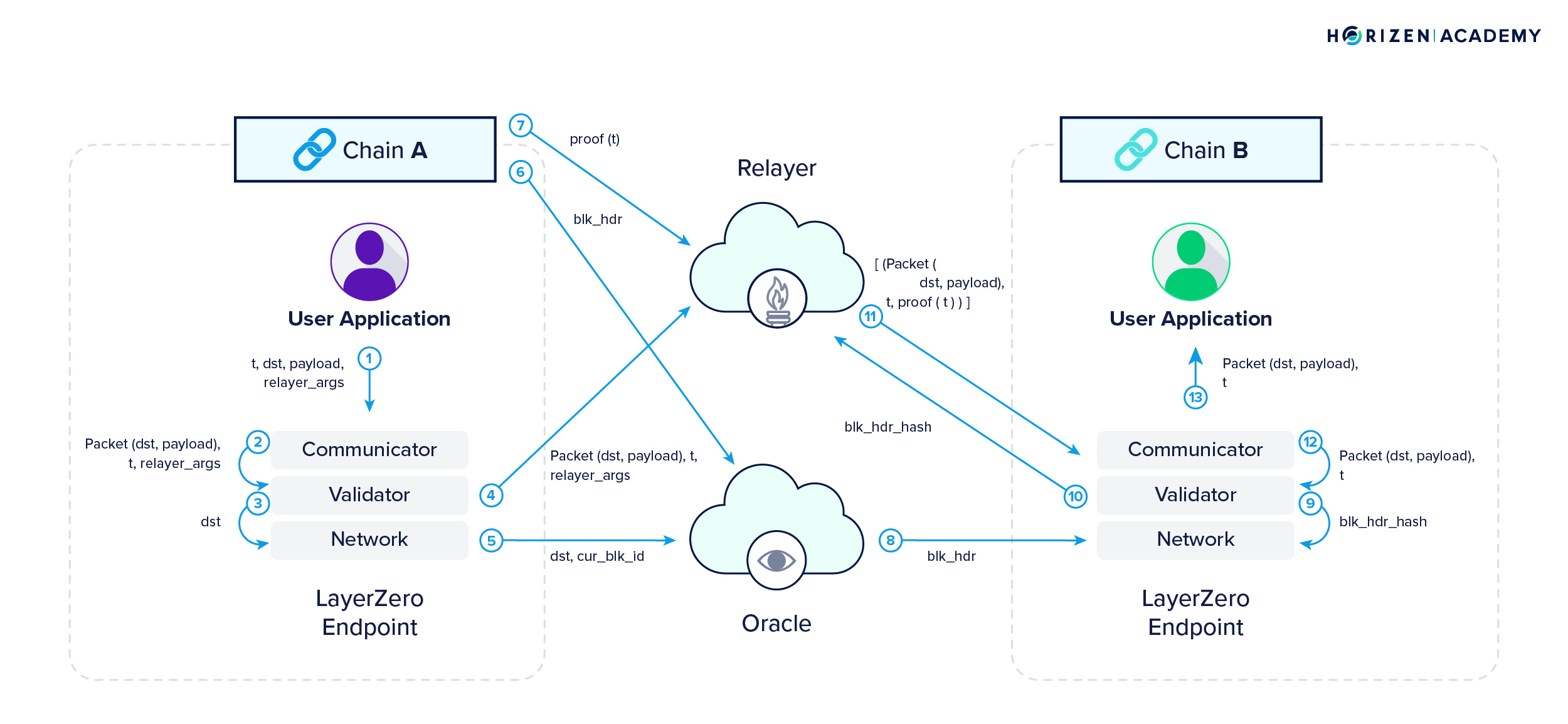
Pros:
- Interoperability: Supports a vast range of blockchains, promoting ecosystem interconnectivity.
- Efficiency: Streamlines the process of cross-chain interactions, enhancing user experience.
- Scalability: Capable of handling increased loads, making it suitable for widespread adoption.
Cons:
- Complex Underlying Technology: May be intimidating for users not well-versed in blockchain technology.
- Reliance on Network Stability: The efficiency and security are contingent on the underlying network’s performance.
- Newer Technology Risks: As a relatively new technology, there may be unforeseen challenges or limitations.
4. Cross-Chain DEX Aggregators
Mechanism: These platforms aggregate liquidity from various decentralized exchanges (DEXs) across different blockchains, facilitating efficient token swaps at optimal rates.
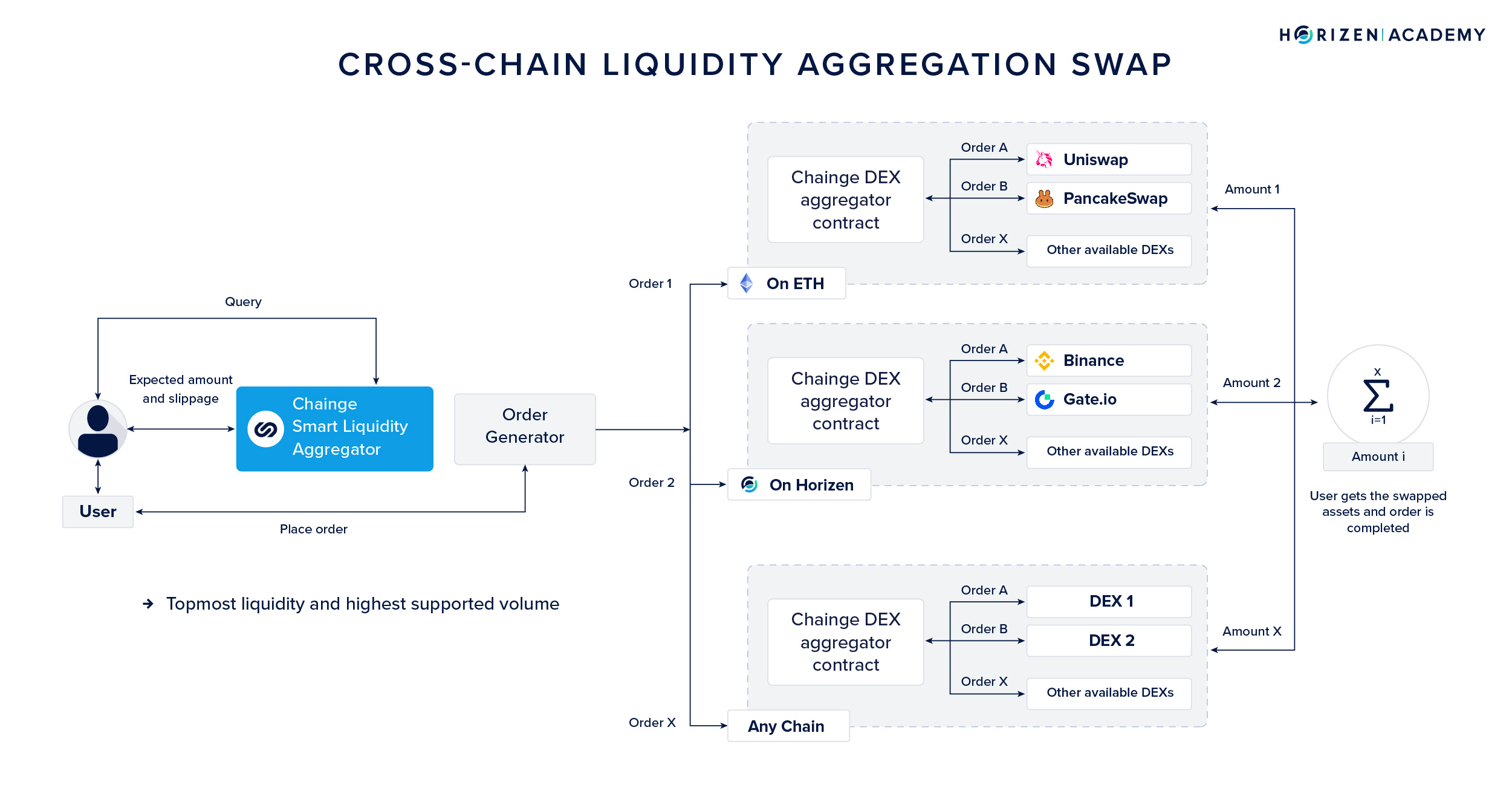
Pros:
- Optimized Trading: Users get the best rates by pooling liquidity from multiple sources.
- Decentralization: Maintains blockchain ethos by aggregating decentralized sources.
- Diverse Asset Support: Access to a wide array of tokens across different blockchains.
Cons:
- Smart Contract Risks: Dependence on the security of underlying contracts across multiple platforms.
- Complexity in Price Discovery: Aggregation from multiple sources can complicate price discovery and order fulfillment.
- Potential for Slippage: Larger orders may face price slippage due to fragmented liquidity.
Top Cross-Chain Swapping Projects
The blockchain ecosystem is witnessing a surge in cross-chain swapping projects, each offering unique solutions to interoperability challenges. We share some of the top projects that are setting new standards in this space.
LayerZero
LayerZero stands out as a robust blockchain messaging protocol. It's not just about connecting over 40 blockchains; it's about the quality of connections it establishes. LayerZero's expertise lies in its ability to facilitate transparent and secure cross-chain messaging from a single interface. This technology has processed millions of messages, showcasing its scalability and reliability.
Axelar
Axelar extends the capabilities of cross-chain communication with its General Message Passing (GMP) capability. This isn't just a bridge; it's a comprehensive solution for cross-chain functionality, allowing developers to call functions across chains seamlessly. It's the flexibility and ease of integration that sets Axelar apart, enabling a rich ecosystem of decentralized applications that can interoperate across various blockchains.
Chainlink
Chainlink's role in cross-chain swaps revolves around its decentralized oracle networks. These networks are pivotal in providing reliable, tamper-proof data for cross-chain transactions. What makes Chainlink a cornerstone in this landscape is its ability to ensure data integrity and security, crucial for maintaining trust in cross-chain operations.
InterPort Finance
InterPort Finance specializes in cross-chain trading with its meta DEX aggregation technology. The platform offers an intuitive approach to swapping tokens across different blockchains, ensuring users get the best rates with minimal slippage. InterPort's commitment to a seamless trading experience makes it a notable player in the cross-chain swap arena.
Horizen EON's Pioneering Implementation of Cross-Chain Swaps
Horizen EON, with its integration of advanced cross-chain technologies, is crafting a new narrative in blockchain interoperability. The platform's approach to cross-chain swaps is multi-faceted, focusing on user experience, security, and efficiency.

Integration with LayerZero
Horizen EON's partnership with LayerZero is a game-changer. This collaboration brings LayerZero's messaging infrastructure into the Horizen ecosystem, enhancing EON's ability to communicate across various blockchains. This integration means more than just messaging; it's about creating a harmonious digital asset ecosystem where decentralized applications can thrive across multiple blockchains.
Strategic Partnership with InterPort Finance
The alliance with InterPort Finance is another strategic move by Horizen EON. Leveraging InterPort's cross-chain trading platform, Horizen EON aims to revolutionize cross-chain and single-chain trading. This partnership underscores Horizen's commitment to building a resilient and interconnected blockchain ecosystem.
Focus on Enhanced Interoperability and User Experience
Horizen EON is not just integrating technologies; it's redefining how users interact with cross-chain swaps.*By bringing together LayerZero’s infrastructure and InterPort's trading solutions, Horizen EON is setting a new standard in user experience. This integration ensures seamless token swaps across blockchains, with an emphasis on security and efficiency.
Conclusion
Cross-chain swaps are revolutionizing blockchain interoperability, breaking down barriers between isolated networks. With innovative projects and platforms like Horizen EON leading the charge, the future of blockchain interconnectivity looks promising. This technology not only enhances user experience but also opens up new possibilities in the world of DeFi and beyond, ushering in a truly interconnected digital asset ecosystem.